Rapid Prototyping
Prostheses
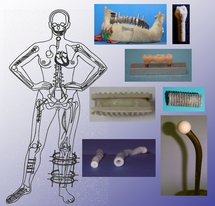
COMPOSITE PROSTHESES MIMICKING THE BIOMECHANICAL BEHAVIOUR OF NATURAL ORGANS
By using continuous fiber reinforced polymers it has been possible to design and manufacture composite prostheses for connective tissue restoration showing a biomechanical behaviour similar to the analogue natural organs.
Glass fibers oriented in a similar fashion of ostheons orientation allowd to manufacture a composite mandible.
By helically wounding grass fiber embedded into an acrylic matrix teeth analogue were produced.
By orienting PET fibers into a hydrogel matrix in a similar fashion of fibers of the collagen fibers of the intervertebral disc a composite analogue was manufactured.
Ligaments and tendon analogues were manufactured by helically winding PET fibers into an hydrogel matrix.
Composite cages for spine fusion were produced by filament winding of carbon fibers into a PEI matrix.
Drop-off plies of carbon and grass fibers mats lead to the manufacture of a composite hip prostheses.
Scaffolds
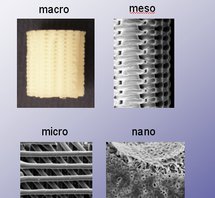
SCAFFOLDS FOR TISSUE ENGINEERING MANUFACTURED THROUGH RAPID PROTOTYPING
Rapid prototyping through additive manufacture process like 3D-photoprinting, bioplotting and ink-jet 3D-printing, allows to produce fully interconnected scaffolds for tissue engineering. Custom made designs, according to the poatient's needs, are ob tained from X-ray CT and MRI imaging.
Scaffolds are made of fully degradable or partially degradable polymers, composites and nanocomposites . The technology and the material design allows a fine control of the structure from the macro-scale to the nano-scale level.
References
- L. Ambrosios et al.
- R. De Santis et al.
- A. Gloria et al.
Patents
- IT-RM
- Italy
- Naples
Copyright © All Rights Reserved